7 Challenges and Solutions of Diesel Engines
- Raktim Das
- Apr 23
- 3 min read
Updated: Aug 14
Be it transport, construction, agriculture, or industrial usage, diesel engines are the backbone of several industries. Mostly known for their durability, fuel efficiency, and torque, these engines are a reliable choice. But even these machines suffer through several challenges. So, it is better to have an idea of the common challenges whether you're operating a commercial fleet or running a generator.
Let’s walk through seven key challenges and their practical solutions.
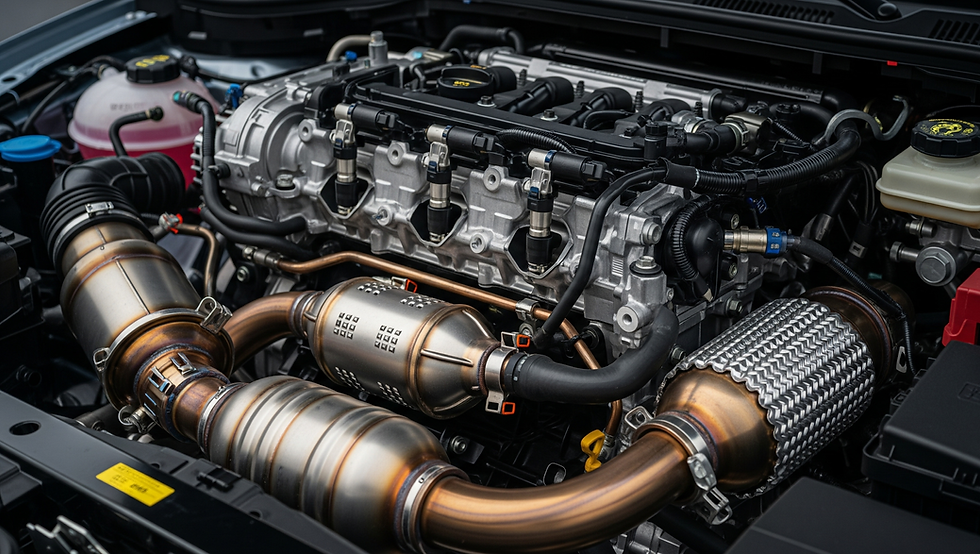
Key challenges of diesel engines and practical solutions
1. Hard Starting or Failure to Start
Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines require heat from compression and glow plugs to ignite fuel. Here are a few things that make it difficult to start the engine:
Cold weather
Worn-out glow plugs
Weak batteries,
Poor fuel quality
It is recommended to first test the glow plugs, if these plugs are old and worn out, replace them. You should also check the battery’s charge, especially in colder months, as diesel engines demand more cranking power to deliver a burst of current to start an engine. Using a winter-grade diesel or fuel additives helps to prevent thickening.
2. Black Smoke from the Engine
The black smoke from the engine run by diesel is toxic for human health and the environment, as it contains unburnt fuel, soot, and other harmful gases. It can be caused by a few factors, including
Incomplete combustion
Clogged air filter
Faulty injectors
Poor fuel quality
Turbocharger issues.
It’s better to start with the basics. For instance, replace or clean the air filter. Next, inspect the fuel injectors for wear or clogging. If the engine is turbocharged, check for signs of oil leakage or mechanical failure. Using clean, high-quality diesel helps avoid soot buildup.

3. Engine Overheating
When carrying over heavy loads, diesel engines need high power, which causes the machine to heat up. But if the temperature needle climbs too high, it may point to coolant leaks, a stuck thermostat, a broken water pump, or a clogged radiator.
Most drivers and operators regularly flush the coolant system and check for leaks. While doing so, make sure the radiator is free from debris and dirt. If you want to avoid sudden breakdown, replace thermostats and worn-out belts as preventive care.
4. Fuel Contamination
Fuel contamination is one of the most common challenges for diesel powered engines. It can occur due to various factors, such as
microbial growth
water condensation
debris or contaminants
As a precaution, operators need to drain water separators frequently. Keeping the container clean and sealed and changing the fuel filters frequently helps to avoid contamination. You can also use biocide additives if microbial growth becomes a problem.
5. Knocking or Rough Idle
Unusual knocking sounds or inconsistent idling often stem from poor timing, injector issues, or worn engine components. Have the fuel injection timing checked and adjusted. Replace faulty injectors and inspect the camshaft or rocker arms for damage. A smooth idle not only sounds better but also prevents long-term wear and tear.
6. Turbocharger Trouble
Turbochargers boost power and efficiency, but they’re also delicate. A worn turbo can cause power loss, whistling noises, or increased oil consumption.
Keep the oil clean, as dirty oil ruins the turbo bearings. Let the engine idle for a few minutes before shutdown to allow the turbo to cool, especially after heavy use. Regular inspection of turbo hoses and intercoolers also prevents leaks and pressure loss.
7. Emission Control Issues
Modern diesel engines use emission systems like DPF (Diesel Particulate Filters), EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation), and SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction). When these clog or fail, engines go into limp mode or shut down altogether.
It’s suggested to stick to the maintenance schedule for DPF regeneration cycles and keep DEF (diesel exhaust fluid) tanks full. Use OEM-grade parts when replacing sensors or valves, and avoid deleting emission systems, which can lead to legal troubles and warranty voids.
Final Thoughts
Diesel engines hold a strong role in many industries. While there might be some challenges, frankly every machine has some of them. Moreover, the issues can be easily resolved by sticking to a routine, using quality parts and fluids, and paying attention to what your engine is telling you.


Great insights on the challenges faced by diesel engines! It’s true that while they are incredibly durable, issues like fuel contamination or poor maintenance can cause significant problems. The same challenges apply when working with excavator spare parts—engine components and systems in heavy machinery need constant care to avoid costly repairs and downtime. Your practical solutions for maintaining diesel engines are useful not just for trucks and generators, but for keeping equipment like excavators running smoothly as well. Thanks for the helpful tips!